
According to estimates, electricity theft and fraud costs the industry as much as $96 billion a year worldwide, with $6 billion in the United States alone. This $96 billion global problem not only raises prices for paying customers and costs taxpayers money, but it also poses a public safety threat in some nations due to dangerous illicit power hookups. High non-technical losses are threatening the financial viability of several countries' energy utilities. For many electric power utilities, the financial losses are important. Lack of profits, a lack of funds for power system capacity and upgrade, and the need to expand generating capacity to cope with non-technical losses can all come from lost earnings. The impact of year-over-year losses has brought several electric utility businesses in the worst-affected countries dangerously close to bankruptcy. Challenges faced- Fraud - When a customer tries to deceive a utility, this is called fraud. Manipulation or physical tampering with the meter to indicate lower readings of power use than the real consumption scenario is a typical traditional practice. Stealing Electricity - By wiring a line from the power source to where it is needed, circumventing the meter, electricity theft can be accomplished. Because the illegal lines are frequently above ground and extremely visible, they are easy to spot. However, instances of utility workers being beaten and requiring police protection to remove the lines are prevalent. Billing Irregularities - Some power companies may be ineffective at measuring the amount of electricity consumed, resulting in an accidental greater or lower figure than the true value. Employees may be persuaded to enter a lower number on the meter than what is displayed. The meter-reader obtains an unofficial wage while the consumer pays a lesser charge. Unpaid Bills - Some persons and businesses do not pay their electricity bills. Chronic non-payers exist in some systems—the exceedingly wealthy and politically powerful who know that their energy will not be switched off whether they pay or not. Poorly maintained equipment- Poor energy management- It leads to high expenses, overloading machines can cause breakdowns or under loading can decrease productivity. Energy Wastage- Not knowing where, when and how the energy is getting consumed or wasted, and also what the reason is for it, whether it is incorrect settings, faulty timers or poorly maintained equipment? Risk of human error- More often than not, industrial operations, devices e.g., reactor, pumps, machinery, etc. operate in silo and data collection related to energy has to be conducted manually which increases the risk of human error and is also tedious and unproductive. Improper data collection- Unavailability of granular data related to energy usage makes it difficult for energy managers to discern energy consumption patterns and results in high GHG emissions, exorbitant utility bills, etc. Major climate goals include making Copenhagen the first carbon-neutral capital by 2025. Copenhagen wants to demonstrate that it is possible to integrate growth, development, and improved quality of life with the decrease of CO2 emissions since the city's population is projected to expand by 20% over the next ten years. The City Council established the ambitious CPH 2025 climate Plan in 2012 to work toward that objective. The four pillars that support the CPH Climate Plan 2025 are: Energy consumption, Energy production, Mobility and City Administration Initiatives. To produce technologies that help the transition away from carbon while fostering green growth, they rely on close collaborations with the business and research sectors. To guarantee that climate and energy thinking is included across all industries, they are making large investments. Many employment are anticipated to be created as a result of these investments, especially in the construction industry. In the long run, the city anticipates that these improvements will lessen the need for investments in additional heating capacity. Copenhagen is influencing the national government to enhance national framework conditions at the same time. The city places a lot of emphasis on setting an example. Copenhagen firmly believes in setting the bar high in order to inspire others to follow suit, notwithstanding the modest amount of emissions generated by the city itself. The main reason for the city's success is a strong political will, a clear determination to achieve this lofty goal at the expense of significant investments and risks; this example should encourage others to have higher ambitions. The IoT affects the energy sector in many ways, it serves the energy industry primarily by providing intelligent options to reduce unnecessary energy by providing more visibility, real – time monitoring where information can be exchanged between utility and its customers. IoT helps energy sector by making it more efficient, secure and greener. You must understand how and where your energy is being consumed before making investment decisions to lower energy expenditures. However, it is still typical in many businesses for electricity usage to be calculated based on the facility's overall energy cost. Digital solutions, on the other hand, can assist you in evaluating the energy consumption of electrical motion equipment, such as motors, generators, and drives, and in identifying opportunities for energy savings and CO2 reductions. When combined with the professional skills required to analyse it, the actual data acquired can assist you in reaching wiser judgments. Inefficiencies can also be found using digital solutions. Data on energy use is continuously acquired from connected motors, generators, drives, and other electrical components in services that are geared toward energy efficiency. This data can be examined in greater detail by knowledgeable service partners to identify inefficiencies and important areas for development. Then they can determine how much energy and money you might be able to save by, say, updating motor systems or putting in variable speed drives. Your service provider can assist you by putting the suggested energy efficiency solutions and services into practise to produce significant energy efficiency gains and CO2 emission reductions. Service providers can also supply energy efficiency solutions utilising various business models, depending on your needs. For instance, they might provide turnkey solutions with distinct energy saving objectives that are carried out at a predetermined time, date, and cost. They could also provide service agreements that share the duty of gradually increasing the energy efficiency of your equipment over time and maximising the return on your assets. These agreements could involve multiyear execution and operational support. These are a few illustrations of adaptable business models that you might use for your operations. Smart grid (SG) introduces a 2-way dialogue where electricity and information can be exchanged between utility and its customers. It is a developing network of automation and new technology and tools working together to make the grid more efficient, reliable, secure and greener. The Smart Grid enables newer technology to be integrated such as wind, solar energy production, and plug-ins electric vehicle charging. AMI enables two-way contact with customers and serves as the smart grid's backbone. Remote meter reading for error-free data, network problem diagnosis, load profile, energy audit, and partial load curtailment in lieu of load shedding are some of the goals of AMI. AMI is made up of a number of hardware and software components that work together to measure energy consumption and transfer data about energy, water, and gas usage to utility providers and customers. The following are the AMI's overarching technology components: Smart Meters: They are advanced metre devices capable of collecting data on electricity, water, and gas usage at various intervals and transferring it to the utility via fixed communication networks, as well as receiving information from the utility such as pricing signals and relaying it to the consumer. Communication Network: Smart metres can provide data to utility companies and vice versa, thanks to advanced communication networks that permit two-way communication. For these applications, networks such as Broadband over PowerLine (BPL), Power Line Communications, Fiber Optic Communication, Fixed Radio Frequency, or public networks (e.g., landline, cellular, paging) are employed. Meter Data Acquisition System: Data is collected from metres over a communication network and sent to the MDMS using software applications on the Control Centre hardware and DCUs (Data Concentrator Units). Meter Data Management System (MDMS)- The metering data is received, stored, and analysed by the host system. Electricity is more costly to deliver at peak times and Smart Grid enables utilities to manage and moderate electricity usage with the cooperation of their customers especially during peak demand times which leads to a reduced operating cost. This also ensures that electricity is more evenly distributed throughout the day. Moreover, Smart Grid technology provides detailed information that allows grid operators to manage electricity consumption in real-time. Greater insight and control reduces outages and lowers the peak power demand. This additionally reduces the need to fire up costly secondary power plants. This includes IoT technologies, big data and advanced analytics with artificial intelligence and machine learning on top, a plethora of communication standards used to send data from one point to another (e.g., from smart metres to utility companies), and additional technologies (digital twins, for example) that we are seeing emerge in the digital transformation of utilities and in Industry 4.0. Building Energy Management System IoT-based analytics tools are the latest advancement in commercial building energy management. An IoT-based platform provides facilities managers with unprecedented levels of insight into their building systems, allowing them to proactively control operations as well as the overall building environment. It is more than a control system because the IoT actually complements traditional building management systems. Facilities managers can use load-shedding schedules to actively and deliberately minimise energy demand (and consequently utility bills) by knowing where, when, and how their building consumes energy. You may collect real-time, detailed information on your business building's energy consumption with wireless IoT sensors deployed throughout the building. These sensors can remotely monitor a variety of tasks, including: Individual machinery Lighting HVAC Ventilation systems Refrigeration units Hot water systems Heat pumps, and more It's possible to design your building's ideal approach to energy management for assured cost savings using the correct data variables—collected, correlated, and evaluated by the IoT. Because the energy consumption of a commercial building is always changing based on a multitude of dynamic conditions—there is no static model of energy use—this IoT-based technique is far more effective for energy management. Better energy management, then, is dependent on obtaining the appropriate data at the right time, which helps building managers to be more flexible and nimble in their energy reduction efforts. The coming of energy dependent era demands the adoption of sustainable energy and optimization of energy. IoT can be the game changer in this area. Its uses include real-time predictive analytics, remote asset management, predictive maintenance and asset utilization. It can reduce costs incurred by equipment failure. IoT has hastened improvement in the sector efficiency. It has shown great growth potential and is likely to play a strategic role in ensuring care, reliance and prudence in the future. In this crusade, DYM Labs is anticipated to serve as a significant aid, unquestionably. Our Internet of Things practice successfully delivers IoT solutions right from integrating the sensors to deriving insights and choosing the suitable platform to the energy sector. We enable them to seize the current business needs and open up a new era of economic growth and competitiveness and provide comprehensive solutions through a global network of specialists and thought leaders. DYM IoT capabilities- DYM Lab’s IoT based EMS monitors consumption for all the energy parameters in real/near-real time, and enables you to benchmark the power consumption of one’s equipment and sends an alert when there is any variation in power utilization. Smart Energy Monitoring System gives the health and performance reports (with the option of customizing the report to your own will) of your plant equipment daily, weekly or monthly. Our solution can be integrated with your current energy meters or any other electrical measuring equipment quite easily also enabling you to measure harmonics of the system allowing for the ability to do bill calculations. We guarantee a secure data storage and a user-friendly UI that can even run-on cell phones. Benefits- Reduce running costs- EMS’s ability to reduce electricity costs by monitoring and optimizing energy used by industrial operations e.g. lighting, heating and cooling, ventilation, reactor etc. Predict energy usage- By collecting energy data, it allows administrators to predict energy usage and budget for the same more effectively. It has built-in cost-saving functions including offering revenue-generating programs, emit ing less power during peak times, and spotting any potential energy leaks. (predict energy usage) Predictive maintenance- Our EMS solution allows users to monitor the issues in real time so that the corrective measures can be taken immediately. For example, a short circuit possibility before it happens get notified to you via an alert. Reduces energy consumption- Your plant's carbon footprint is the entire amount of greenhouse gases produced and is directly related to the amount of energy it uses. Having DYM Lab’s solution in place to regularly monitor and manage this can aid in identifying energy system flaws that can be fixed to decrease your influence on the environment. Last but not least, companies across the globe are promoting the environmental improvements they have made to their operations, and adherence to various compliances. Implementing an energy management system would not only be environment friendly and sustainable but also improve the perception of your brand among various shareholders. Any business that wants to be competitive in a dynamic environment must embrace digitalization, which is a necessary component of the difficulties encountered across the market structure and when addressing the human factor. The IoT has far more promise than just data gathering and accurate prediction. Don't get me wrong, predictive analytics and data analysis are important parts of any good IoT deployment. However, there is more to it, and this is what gives rise to the phrase "Industry 4.0" and the "industrial revolution" that everyone refers to. Beyond simply linking factories, machines, and sensors to the internet and automatically collecting data, advanced IIoT systems do much more. These solutions go beyond simple IoT by offering recommendations for production-wide improvement that are based on AI. To put it another way, certain intelligent Internet of Things (IoT) solutions gather data, issue alarms, AND offer actionable insights based on the data, assisting humans in making better decisions, committing fewer errors, and maintaining quality while supporting much larger production scales. At DYM Labs we- INSPIRE : Inspired from democratizing the technology for easy availability, accessibility and affordability IDEATE : Constant inspiration has led us to Ideation of our IoT Platform and encouraged our first set of Industrial customers taking a big leap with us IMPLEMENT : With the strong footing in IoT platform, DYM Labs is now striving towards Implementing an IoT Marketplace which will have modular IoT services for every player in IoT Value Chain. We adapt the agile methodology as it is a sophisticated approach to IoT adoption that successfully addresses the issues of bringing connecting culture and technology together. This architecture divides an IoT installation into sprints, which are tiny, easily limited tasks with short time horizons. In contrast to longer, open-ended executions, which can result in a full culture shock, sprint projects can let stakeholders envisage a large-scale implementation in a tangible, intimate environment, then work to scale it over time. Any project necessitates precise tuning and rapid responsiveness to change, which demands close collaboration among project teams. While different departments may be focused on different activities, they all have the same goal. IoT efforts rely heavily on enhanced transparency between operational and information technology divisions. Teams are encouraged to collaborate on products in novel ways, resulting in shorter lead times, increased overall development efficiency, and more product updates and releases. References https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/full/10.1155/2014/974682 https://www2.deloitte.com/us/en/insights/focus/internet-of-things/iot-in-electric-power-industry.html https://www.kelltontech.com/kellton-tech-blog/impact-iot-energy-sector https://embapro.com/frontpage/pestelcase/15443-grid-smart https://www.biz4intellia.com/blog/favoring-iot-technology-to-monitor-industrial-energy/ https://www.inenco.com/insight/blog/how-will-iot-and-big-data-contribute-to-the-energy-sector/ https://www.iot-now.com/2021/10/05/114222-energy-management-system-4-0/ http://poweramr.in/smart-metering-dlmshttps://www.sightline.org/2020/05/18/playing-monopoly-or-how-utilities-make-money/ https://mediaindia.eu/business-politics/power-theft-continues-to-hit-indian-economy/ https://inductiveautomation.com/resources/article/what-is-scada https://www.networkedenergy.com/en/news-events/energy-theft-and-fraud-reduction?utm_medium=sei&utm_source=external&utm_campaign=article%20f&t https://www.smart-energy.com/industry-sectors/energy-grid-management/energy-theft-and-fraud-reduction/ https://www.thehindu.com/news/national/karnataka/the-smart-meter-solution-to-the-problem-of-power-theft/article5186952.ece https://www.elprocus.com/power-theft-prevention-techniques/ https://www.i-scoop.eu/industry-4-0/smart-grids-electrical-grid/ https://indiasmartgrid.org/Advanced-Metering-Infrastructure.php https://www.iotacommunications.com/blog/building-energy-management-system/ https://blog.ipleaders.in/electricity-theft-punishments-india/ https://www.smart-energy.com/industry-sectors/energy-grid-management/energy-theft-and-fraud-reduction/ https://www.energyefficiencymovement.com/en/3-ways-digital-solutions-can-reduce-energy-costs/ Thanks to DYM Labs Team Chetna Ahlawat Rupal Kargeti
Read more →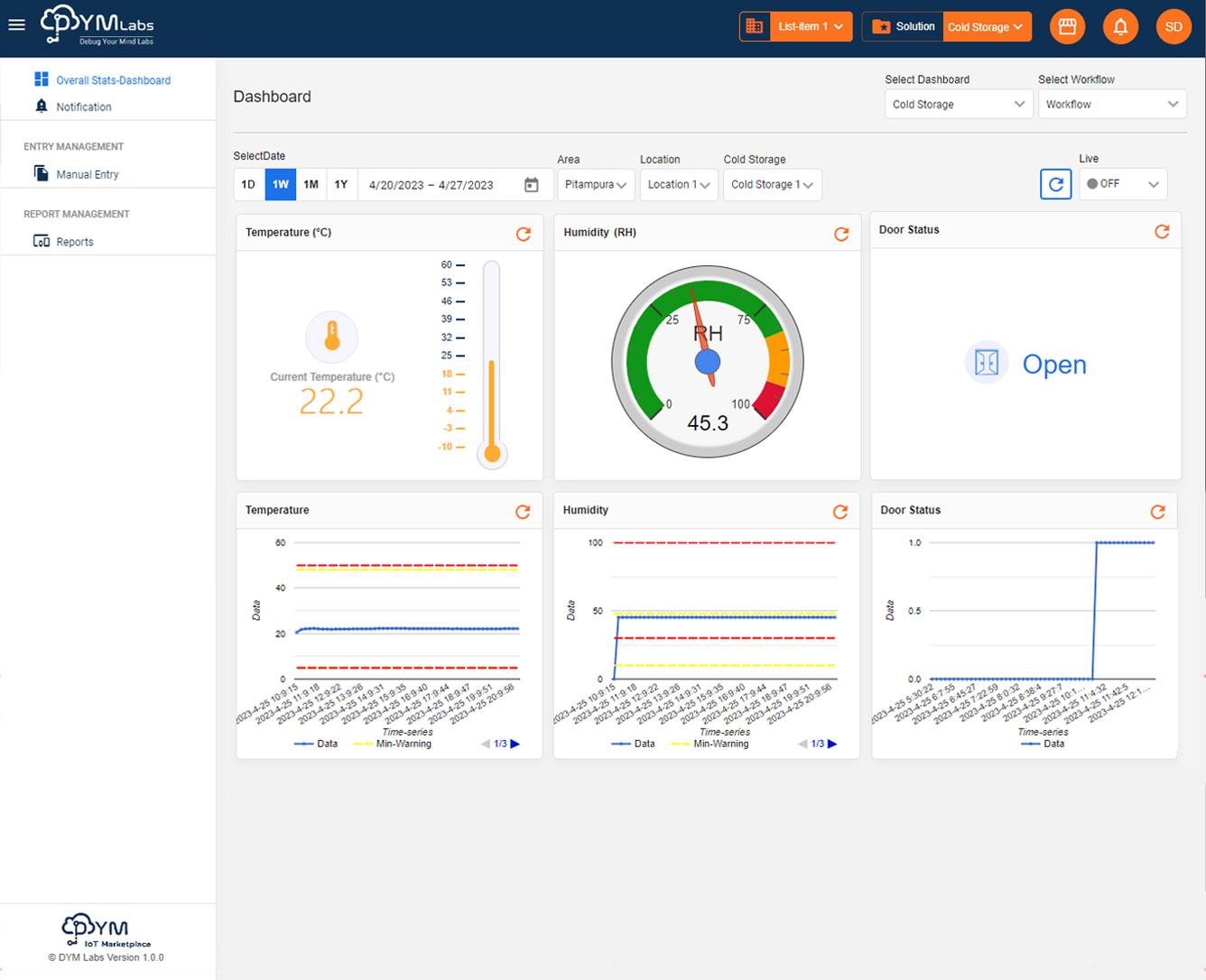
Almost everyone consumes perishable goods daily. Fruits, vegetables, dairy goods, meat and poultry, fresh and frozen foods, fish, and even pharmaceuticals are among these products. For example, milk typically moves from the cows via pipes connected to cooling storage tanks, also located on the farm and that is where the cold chain begins. Milk remains in the storage tanks, where it’s kept at below 40 degrees Fahrenheit for no more than 48 hours. Tanker trucks pick up and transport the milk to a dairy processor, where it’s tested to ensure it has been properly chilled, and is free of bacteria. Any milk that fails is discarded. Milk theft, the spread of disease, and mistrust between farmers and insurance companies are a few of the issues that this industry is grappled with. Transporting millions of litres of milk every day is not an easy feat. Fresh milk is collected from the dairy farm and then driven to a local dairy processing plant in an insulated, sealed tanker truck. These insulated trucks keep the milk at the optimal temperature throughout the journey. Chilled trucks are used to transport processed Dairy products such as Paneer, Cheese, Butter, etc. Advent of comprehensive technology offers temperature monitoring solutions to keep your milk at an optimal temperature as well as help to prevent the theft from happening ahead through robust tracking solutions. There is so much more information that needs to be tracked and analyzed than just temperature. Cold chain requires a 360-degree approach to Fleet Management; some of which include: fuel monitoring, load monitoring, On-Board diagnostics, live tracking, dashboards for detailed analysis and RFID/Biometrics. Ensuring that a shipment will remain within the temperature range for an extended period depends mainly on the type of container used and the refrigeration method. Cargo refrigeration takes up approximately 20% of all energy consumed in cold chain logistics. Other factors such as duration of transit, the size of the shipment, and the ambient or outside temperatures experienced are essential in deciding what type of packaging is required and the related level of energy consumption. In addition to merely wanting to provide consumers with the safest, highest-quality product possible, sectors like food and pharmaceuticals must use cold chain monitoring and data logging from manufacturing onward to comply with federal requirements. The tricky part about such perishable goods is that they have to be taken special care of. This is simply because if they do not reach on time, they risk expiry, and at the very least, loss of quality. And it’s not about just time, for them to be transported without damage, special measures need to be taken that ensure a safe environment and passage for such goods. It is crucial to guarantee their safety, quality and make sure that the room's temperature never rises above the ideal level. Many industries have been dependent on temperature-controlled conditions to maintain the quality of their perishable products for which they have been using cold storage facilities for decades. But with global shortages affecting every aspect of the supply chain, these facilities are more in demand than ever. Monitoring these facilities is not an easy task, but the emergence of new technologies has made it quite convenient. What are the common challenges faced by a cold storage owner? Energy Wastage: Optimising energy usage and monitoring refrigeration equipment in cold storage facilities has become increasingly important to warehouse managers. Energy costs typically account for 15% or more of a warehouse's operating budget, and the lack of data on how much you are being charged for energy doesn’t help either. Compressor and equipment health: Constantly being concerned about equipment breaking down, compressor health or unintentionally producing significant demand increases becomes time-consuming and challenging. Maintaining ideal conditions: Precise temperatures, pressure, and humidity for refrigerators and cold rooms’ information, wherever you are, to ensure your settings are within acceptable limits. The need for perfect conditions throughout your whole business, so that the employees can focus less on monitoring and more on the things that matter. Lack of real-time monitoring: Not getting notified of the temperature fluctuations and power outages, can lead to asset loss or audit failures. Stock management: Ensuring that all empty spaces are filled with stock as much as possible can take a lot of resources and time which otherwise could have been better utilized. In our multiple interactions with cold storage owners/managers and after some site visits, we got to see what are the pain points in cold storage, from lack of real-time monitoring to lack of equipment maintenance, from human errors due to lack of digitization to microbial growth and many more… To counter these issues, DYM Labs has created an IoT-based cold storage monitoring system tailored to the product which leads to the optimum utilization of space and resources. It helps you track the usage pattern and power consumption of devices, minimize wastage, detect anomalies within the facility, and monitor and control the intensity of light as per the changes in daylight. An IoT-enabled monitoring solution that brings terrific value to businesses and enhances profitability. Some of the benefits that cold storage owners will experience after the implementation of our no-code IoT platform are – Energy Efficiency: Overall energy expenditures can be decreased with precise temp adjustments to maintain stringent temp ranges (especially for products in different zones in the warehouse). Real-time monitoring: Monitoring key parameters in real-time identifies variances when they change from their pre-set values; correcting these immediately minimizes product losses. Stock management: Our cold storage management system informs managers where the empty spaces are within a cold storage warehouse for more effective stocking of products, thereby increasing capacity and throughput. Audit trails: Our CSM captures data on storage, and analytics provides the documentation required to satisfy regulatory audits, and customer questions, or to expedite recall investigations, if needed. Product quality: Temperatures are monitored and adjusted as needed in real-time, which greatly improves the quality, safety, and longevity of refrigerated products. The journey of million miles starts with a single step and by leveraging our IoT-enabled monitoring solution, you will be able to overcome the loss of perishable commodities in cold storage through real-time monitoring. Remote monitoring solutions will further improve the maintenance efficiency of probes and sensors whenever the value from the device deviates beyond acceptable limits. The data that is gathered over time will assist in identifying the ideal storage conditions and the distribution of temperature inside the cold storage facility. This will make it easier for facility managers to locate the hot and cold spots in a cold storage facility and ensure that perishable goods are stored in a way that will preserve their quality throughout a long-term supply of goods. One can see how many invaluable insights are opened to us from data gained which opens multiple dimensions like monitoring energy theft, achieving carbon emission monitoring, and many more. All in all, it enables the business owner to ensure that everything is ideal throughout their cold storage so that staff can concentrate less on monitoring and more on important items. Our Cold Storage Monitoring solution will send an alert whenever sensors identify substantial temperature, humidity, power swings, and many KPIs with real-time monitoring of numerous points. To know more about how IoT-enabled cold storage monitoring helps to increase your ROI, please talk to our experts.
Read more →
In today's rapidly advancing technological landscape, the integration of the Internet of Things (IoT) has revolutionized the way we interact with our surroundings. From smart buildings to home automation systems, IoT has played a pivotal role in reshaping the concept of living and working spaces. Let's delve into how IoT has driven the evolution of smart buildings, Building Management Systems (BMS), and smart homes, creating a more interconnected and efficient world. 1. Smart Buildings: Beyond Conventional Boundaries IoT has propelled smart buildings into a new era of intelligence and efficiency. Gone are the days of static structures; IoT-enabled sensors and devices have empowered buildings to adapt and respond to real-time data. Heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems adjust based on occupancy levels, optimizing energy consumption and enhancing comfort for occupants. 2. Building Management Systems (BMS): Orchestrating Efficiency BMS has embraced IoT to orchestrate an unparalleled level of efficiency in building operations. Sensors and actuators communicate seamlessly, collecting and analyzing data that allows for predictive maintenance. This proactive approach helps prevent equipment failures and reduces downtime, saving both time and resources. 3. The Rise of Smart Homes: A Personalized Living Experience IoT's integration with smart homes has redefined the way we experience our living spaces. Smart thermostats, lighting systems, and security cameras can all be controlled remotely through smartphones. This not only enhances convenience but also contributes to energy conservation by allowing users to monitor and adjust energy usage in real-time. 4. Energy Management and Sustainability IoT-driven advancements have also been instrumental in promoting sustainability. Smart buildings equipped with IoT sensors monitor energy consumption patterns and can identify areas for optimization. Lighting and HVAC systems adjust based on natural light availability and occupancy, minimizing energy waste. This not only reduces operational costs but also supports environmental conservation efforts. 5. Enhanced Security and Safety IoT's impact extends to security and safety within smart buildings and homes. Integrated security systems utilize sensors, cameras, and access control mechanisms to provide comprehensive monitoring. In case of any suspicious activity or emergencies, automated alerts are sent to both occupants and authorities, ensuring a swift response. 6. Data-Driven Insights: Informing Future Design The wealth of data collected by IoT devices is a goldmine for architects, designers, and engineers. Analyzing user behavior and building performance data allows for data-driven design decisions. Architects can optimize layouts based on space utilization patterns, leading to more functional and efficient designs in the future. 7. The Path Forward: Continual Innovation As technology evolves, so too will the impact of IoT on smart buildings, BMS, and smart homes. Advancements in edge computing, machine learning, and AI will further refine and expand the capabilities of IoT-enabled systems. This promises to bring even more sophisticated automation, personalization, and energy efficiency to our built environment. In conclusion, IoT's integration has ushered in a new era of intelligence, efficiency, and convenience in the realm of smart buildings, BMS, and smart homes. As architects, engineers, and technologists collaborate to harness the power of IoT, the evolution of our living and working spaces holds exciting potential. Embracing this interconnected future is not just a technological advancement, but a leap towards a smarter, sustainable, and safer world. #IoTInnovation #SmartBuildings #ConnectedLiving
Read more →